GRUB for DOS is the dos extension of GRUB. It enables dos users to run the configuration console directly in real mode. The project also contains an utility called WINGRUB, an GUI intends to help configuring and installing GRUB in the WINDOWS environment. Grubinstgui.exe Can`t Run Background Program 7/16/2019 GitHub is home to over 36 million developers working together to host and review code, manage projects, and build software together. Right click grubinstgui.exe and run as Administrator. Select your flash drive or hard disk based on the size of the device. (1024 MB = 1 GB) Click install. Copy grldr and menu.lst to the drive. Right click menu.lst and click edit or “Open With” and select Notepad. Grubinst Gui.exe 1.1 The Luscher Color Test Pdf: software, free download Map Dota Naruto Vs Bleach Vs One Piece Ai Terbaru Spolszczenie Do Avatar The Game Chomikuj Pl Video Yanmar 2gm Cooling Update Action Replay Max Ps2 Usb Utilities Blueprint Oneworld User Manual Laser Defender Game In Unity3d Assets. 如果您的系统提示“找不到grubinstgui.exe”或“grubinstgui.exe缺失” 或者“grubinstgui.exe错误”等等,请不用担心,在本页使用迅雷。下载到该DLL文件后用WinRAR解压缩直接拷贝到原目录即可解决错误提示!希望我们提供的grubinstgui.exe对您有所帮助!.
beanPost at 12-4-2007
Latest version maintained at:http://grub4dos.sourceforge.net/wiki/index.php/Grub4dos_tutorial
GRUB for DOS is an universal boot loader based on GNU GRUB. It can boot offDOS/LINUX, or via Windows boot manager/syslinux/lilo, or from MBR/CD. Italso has builtin BIOS disk emulation, ATAPI CDROM driver, etc.
First of all, GRUB for DOS has a flexible boot loader. Unlike GNU GRUB whichrelies on three stages of files to boot, GRUB for DOS uses a much bettersolution. The main function of GRUB is placed in a single file grldr, whilethe boot loader is placed in another file grldr.mbr, which can be installedto MBR or partition boot sector. At startup, boot code in grldr.mbr willdynamically scan the root directory of every local partition for grldr, andload the first one found. Using this scheme, the location of boot file is nolonger fixed, users can move it across partition boundary without causingbooting problems.
Secondly, GRUB for DOS can be loaded in multiple ways. GRUB for DOS runtimeimage comes in two forms. One is grldr, which can be loaded by MBR/partitionboot sector and the Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista boot manager. It can alsoact as the eltorito boot file for bootable CDROM. The other is grub.exe,which is a hybrid executable that can be launched from linux console and DOSprompt.
Thirdly, GRUB for DOS extends the function of GNU GRUB. The most significantenhancement is the map command. In GRUB for DOS, the map command can be usedto create virtual harddisks and floppies from image files. These virtualdevices can be accessed even after DOS starts.
There are other useful features of GRUB for DOS which are not present in GNUGRUB, such as ATAPI CDROM driver, Chinese support, and so on.
There are many ways to install GRUB for DOS. Some of them requires modifyingMBR or partition boot sector, while others requires changing system startupconfiguration files.
You can use bootlace.com or grubinst.exe to install GRUB for DOS boot codeto MBR:
bootlace.com can be used in DOS, Windows 95/98/Me and Linux. Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of first hard drive under DOS,Windows 95/98/Me:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of IDE channel 0, primary driveunder Linux:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of hard drive image file aa.dsk:
grubinst.exe can be used in Linux, FreeBSD and Windows NT family OSs(Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/Vista). Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of first hard drive under WindowsNT family OSs:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of IDE channel 0, primary driveunder Linux/FreeBSD:
You can also use device names:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the MBR of hard drive image file aa.dsk:
There are many options you can use with bootlace and grubinst, use the -hoption to display help message.
After installing the boot code, you need to copy grldr and menu.lst to theroot directory of any FAT16/FAT32/NTFS/EXT2 partition.
2.2 Install GRUB for DOS boot code to partition boot sector
You can use grubinst to install GRUB for DOS boot code to partition bootsector. Examples:
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the first primary partition of the firsthard drive:
or
or grubinst -p=0 (hd0)
Install GRUB for DOS boot code to the first primary partition of the harddrive image file aa.dsk:
or
Just as in GRUB, extended partition starts with (hd0,4).
After installing the boot code, you need to copy grldr and menu.lst to thepartition which you install the boot code on.
You can use load GRUB for DOS in config.sys using one of the following lines:
grub.exe can also be launched from DOS prompt or batch file such asAUTOEXEC.BAT.
First, you need to apply the kexec patch to the Linux kernel.
Then, you can use the following commands to launch GRUB for DOS from linux:
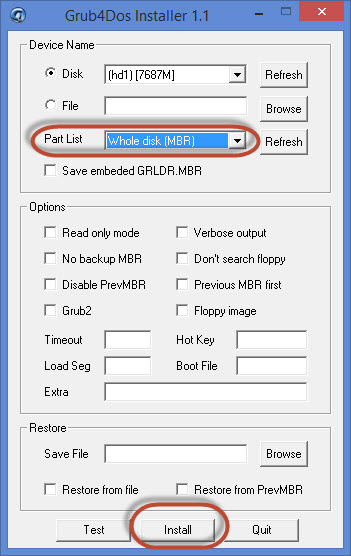
2.5 Booting GRUB for DOS via the Windows NT/2000/XP/2003 boot manager
Add the following line at the end of boot.ini (this file is hidden):
Grubinst_gui.exe Free Download
Then copy grldr to C:, and create the GRUB4DOS configuration file atC:menu.lst.
Next time you start windows, there is a new option 'Start GRUB4DOS' whichcan be used to start GRUB for DOS.
2.6 Booting GRUB for DOS via the Windows Vista boot manager
Use bcdedit to configure the startup menu:
Then copy grldr.mbr to C:, grldr and menu.lst to the root directory of anyFAT16/FAT32/NTFS/EXT2 partition.
grldr.mbr can also be used to start GRUB for DOS in Windows NT/2000/XP/2003(in fact, grldr.mbr is basicly the first 16 sectors of grldr). To usegrldr.mbr as the boot file, use the following line in boot.ini:
As in Windows Vista, you need to copy grldr and menu.lst to the rootdirectory of any FAT16/FAT32/NTFS/EXT2 partition.
grub.exe can be loaded as a linux kernel.
Load GRUB for DOS using GRUB or another copy of GRUB for DOS, add thefollowing section to menu.lst:
Load GRUB for DOS using syslinux, add the following section to syslinux.cfg:
3. Booting DOS/Windows 9X/Windows NT startup files
In GRUB for DOS, you can load the DOS/Windows 9X/Windows NT startup filesdirectly.
DOS, Windows 95/98/Me:
Windows NT/2000/XP/2003:
Windows Vista:
In GRUB for DOS, disk emulation is implemented using the 'map' command.
Here is an example of mapping a image file as virtual floppy, and boot from it:
map —hook is used to make the mapping created by first map command takeeffect immediately.
Here is an example of booting from the virtual hard disk:
Map the image file as virtual hard disk, but boot from the original disk:
CDROM emulation is not implemented.
In direct mapping, the image file must be contiguous.
The virtual disk is implemented using INT 13. Therefore, it can be accessedin system that still uses INT 13, such as all kinds of DOS and Windows 9X(compatible mode disk access), and it can't be accessed in system that usesprotected mode drivers, such as Linux, FreeBSD and Windows NT family OSs.
Indirect mapping is very similar to direct mapping, here is an example:
The —mem option indicates indirect mapping.
In indirect mapping, the image file is copy to memory before the mapping isapplies, therefore, the image file need not to be contiguous, however, youmust have enough memory to hole the image file.
To create virtual hard disk, you need an image file that resemble a realhard disk, which consist of MBR and partition data. If the image file onlycontains partition data, you need to patch it with MBR to create disk image.
Grubinst_gui.exe
GRUB for DOS has taken this into consideration. When mapping disk imagefile, it will test the presence of MBR, if not found, it will create MBRautomatically using the partition data. For example:
aa.dsk can be either disk image or partition image, in the later case, GRUBfor DOS will create the MBR in the air.
The indirect mapping of GRUB for DOS is similar to the function of externaltool memdisk from syslinux. In fact, the following two menu entries doroughly the same thing:
However, memdisk does not support direct mapping or auto MBR creation.
Use the following command to initialize ATAPI CDROM:
Then, use the following command to start using ATATPI CDROM:
After cdrom —hook, the CDROM device can be accessed using (cd0), (cd1), etc.
To boot from the first CDROM, use the following commands:
To stop using CDROM:
The first command removes the (cdN) device mapping, while the second onestops the CDROM driver.
If you boot GRUB for DOS from CDROM, the booting device will be(cd). This device is always accessible. |
However, if you want to access file from other CDROMs, you still need toinitialize them using the above commands.
Examples:
To boot from the first CDROM:
In GRUB for DOS, you can use grldr to create bootable CDROM:
grldr and menu.lst should be placed at the root directory of CDROM image.
The above two commands can both create a bootable CDROM, but they are nottotally the same.
The first one tells BIOS to load the whole grldr. However, some buggy BIOSmight ignore it and load only a portion of the file, typically one sector(2048 bytes). This will cause the program to fail.
The second one tells BIOS to load only the first sector (2048 bytes), andthe program loads the rest from CDROM. This method is safer, it should workfor most BIOS.
you can optionally use the -boot-info-table option, but the info tablewill be ignored by the program. |
Grubinst_gui
To load GRUB for DOS from BCDW, first copy grldr and menu.lst to the rootdirectory of CDROM image, then add a new
Grubinst_gui
line to the [MenuItems] section of BCDW configuration file bcdw.ini:
documented on: 2007-10-21